Genomics is making great strides thanks to the power of cloud computing. Today the Human Genome Sequencing Center (HGSC) at Baylor College of Medicine and DNAnexus announced a broad  collaboration focused on advancing the state-of-the-art in the large-scale clinical analysis of genomic data.
collaboration focused on advancing the state-of-the-art in the large-scale clinical analysis of genomic data.
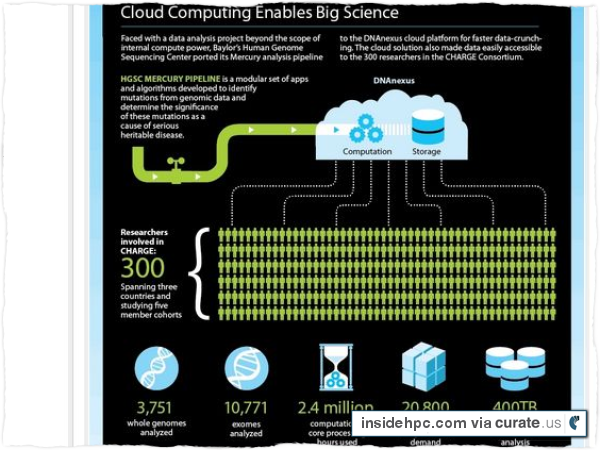
The management and analysis of genomes at the scale needed to appropriately power clinical studies requires computational infrastructure that exceeds the capacity of most institutional resources,” said Jeffrey Reid, Ph.D., Assistant Professor, Department of Molecular and Human Genetics, Baylor College of Medicine. “Working with DNAnexus and Amazon Web Services, we were able to rapidly deploy a cloud-based solution that allows us to scale up our support to researchers at the HGSC, and make our Mercury pipeline analysis data accessible to the CHARGE Consortium, enabling what will be the largest genomic analysis project to have ever taken place in the cloud.”
The CHARGE project involves more than 300 researchers across five institutions around the world analyzing the genome sequence data of over 14,000 individuals (3,751 whole genomes and 10,771 exomes), requiring approximately 2.4 million core-hours of computational time and some 860 TB of storage. At the project’s peak, HGSC used the DNAnexus platform to spin up more than 20,000 cores on-demand in order to run the CHARGE data through the Mercury analysis pipeline. During this period, HGSC was running the largest genomics analysis cluster in the world, hosted by AWS.
Read the Full Story.