This article is part of the Five Essential Strategies for Successful HPC Clusters series which was written to help managers, administrators, and users deploy and operate successful HPC clusters while preparing for HPC Cloud.
Cloud computing offers certain flexibility not normally found in fixed-size, on-premise HPC clusters. Users with existing clusters can elastically expand (then contract) their capacity without large capital costs or set-up time. Those without clusters now have the capability to quickly spin-up HPC resources in the Cloud. While there are many Cloud providers, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and some others offer true HPC clouds that can deliver the type of computing environment that high performance applications require.
 Integrating a Cloud solution into an in-house cluster can be difficult because the Cloud only provides the raw machines to the end users. Similar to an on-site cluster, the Cloud cluster needs to be configured and provisioned before use. All of the issues mentioned previously, from software complexity to system growth and scalability, as well as heterogeneous environments, need to be addressed before any meaningful HPC Cloud work can begin. Indeed, flexibility and ease of management is now even more important in the Cloud due to the ephemeral nature of Cloud clusters, (i.e., administrators may need to repeatedly set up and tear down Cloud instances over time). Long lead times for custom cluster configuration defeats the advantages of an on-demand Cloud environment.
Integrating a Cloud solution into an in-house cluster can be difficult because the Cloud only provides the raw machines to the end users. Similar to an on-site cluster, the Cloud cluster needs to be configured and provisioned before use. All of the issues mentioned previously, from software complexity to system growth and scalability, as well as heterogeneous environments, need to be addressed before any meaningful HPC Cloud work can begin. Indeed, flexibility and ease of management is now even more important in the Cloud due to the ephemeral nature of Cloud clusters, (i.e., administrators may need to repeatedly set up and tear down Cloud instances over time). Long lead times for custom cluster configuration defeats the advantages of an on-demand Cloud environment.
In addition, because Cloud use is metered, monitoring cloud activity is vitally important. Unmonitored Cloud use can result in Cloud budget overruns and added expense.
From a user’s perspective, the Cloud cluster needs to look as much as possible, like the existing cluster so they are not burdened with learning new system rules. In a sense, the end user should not be able to tell the difference (other than perhaps data transfers) between Cloud and cluster nodes.
An integrated solution like Bright Cluster Manager, shown in Figure 4, can provide a managed and transparent Cloud-based HPC cluster. The same powerful cluster provisioning, monitoring, scheduling and management capabilities that Bright Cluster Manager provides to onsite clusters extend into the cloud, ensuring effective and efficient use of the virtual cloud resources. Using Bright Cluster Manager, you can extend into public clouds, such as AWS, with only a few mouse clicks. There’s no need for expert knowledge of Linux or Cloud computing. The exact same administration interface is used for both local and cluster nodes. Installation/initialization, provisioning, monitoring, scheduling and management are identical. In this scenario, there is no learning curve required for Cloud HPC use.
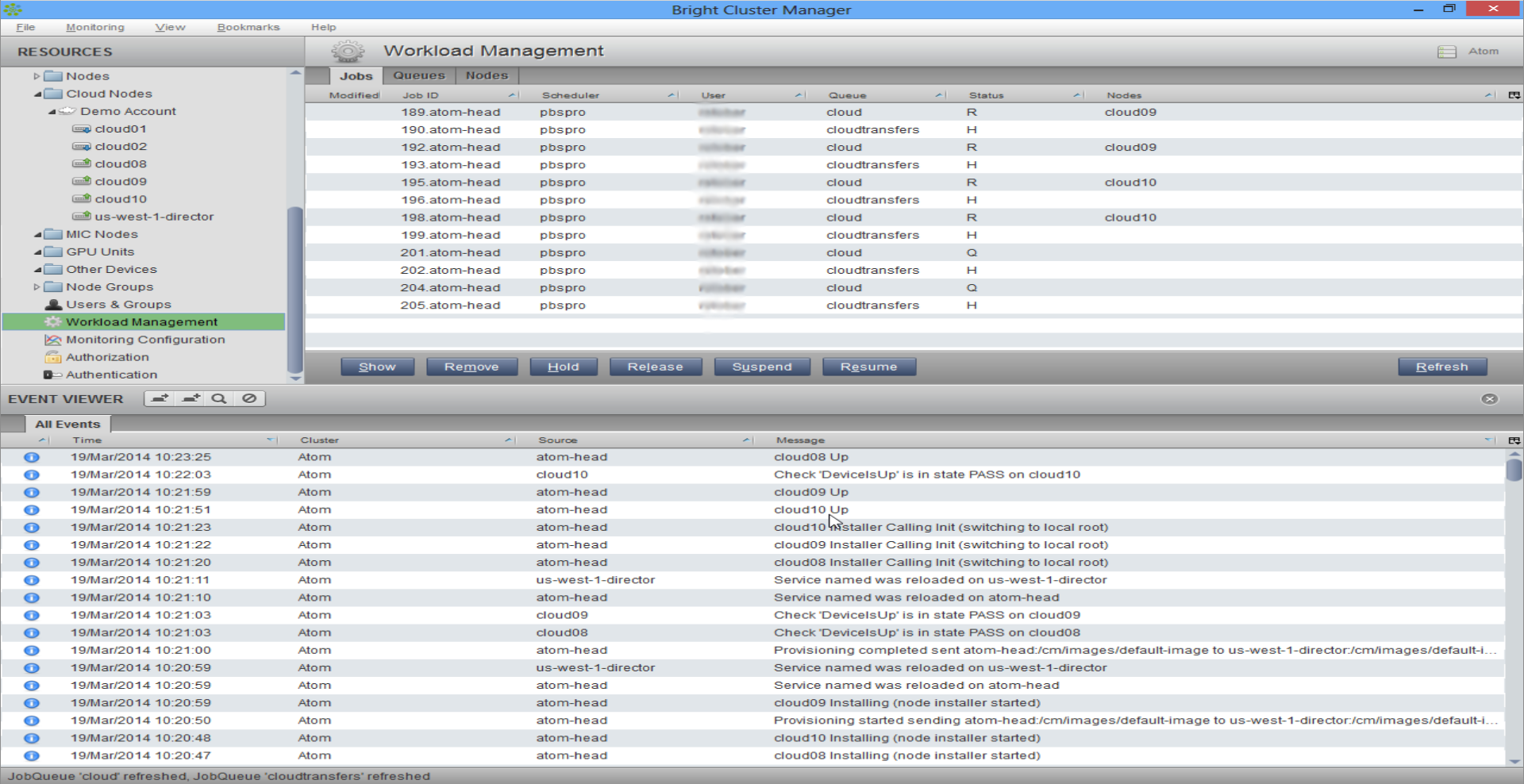 Bright Cluster Manager manages nodes on the ground and in the cloud. Managed HPC workloads are running here on the ground and in the cloud via Bright and the PBS Professional workload manager.
Bright Cluster Manager manages nodes on the ground and in the cloud. Managed HPC workloads are running here on the ground and in the cloud via Bright and the PBS Professional workload manager.
Recommendations for HPC Cloud
- Cloud HPC offers an elastic and flexible method to expand your HPC capabilities. Make sure you use Cloud services that are designed for HPC applications including high-bandwidth, low-latency networking, exclusive node use, and very high compute and storage capacities.
- Develop a very flexible and rapid provisioning scheme so that you can spin-up clusters in the Cloud quickly. This environment should mirror your local systems as much as possible and be tested before you allow users to make use of the Cloud. Improperly configured Cloud instances may cause user jobs to fail silently while the “Cloud meter” keeps running.
- Monitoring is essential. Keep a close eye on Cloud usage to avoid unexpected costs.
- Integration with existing workload schedulers is essential so that users are not burdened with new procedures or rules for using Cloud resources.
- Consider the capabilities of Bright Cluster Manager where your existing cluster can be seamlessly expanded into the Cloud. The new capacity is managed in the same way as your existing cluster and users can start using these new resources immediately with minimal set-up.
Next week’s article will look at Managing a Hadoop Cluster. If you prefer you can download the entire insideHPC Guide to Successful HPC Clusters, courtesy of Bright Computing, by visiting the insideHPC White Paper Library.




