In this week’s Sponsored Post, Michael Kagan, the Chief Technology Officer of Mellanox Technologies, looks at the explosion of data and how RDMA based protocols can speed up the storage network bottlenecks.
With the explosion of data over the past few years, data storage has become a hot topic among corporate decision makers. It is no longer sufficient to have adequate space for the massive quantities of data that must be stored; it is just as critical that stored data be accessible without any bottlenecks that impede the ability to process and analyze data in real time.
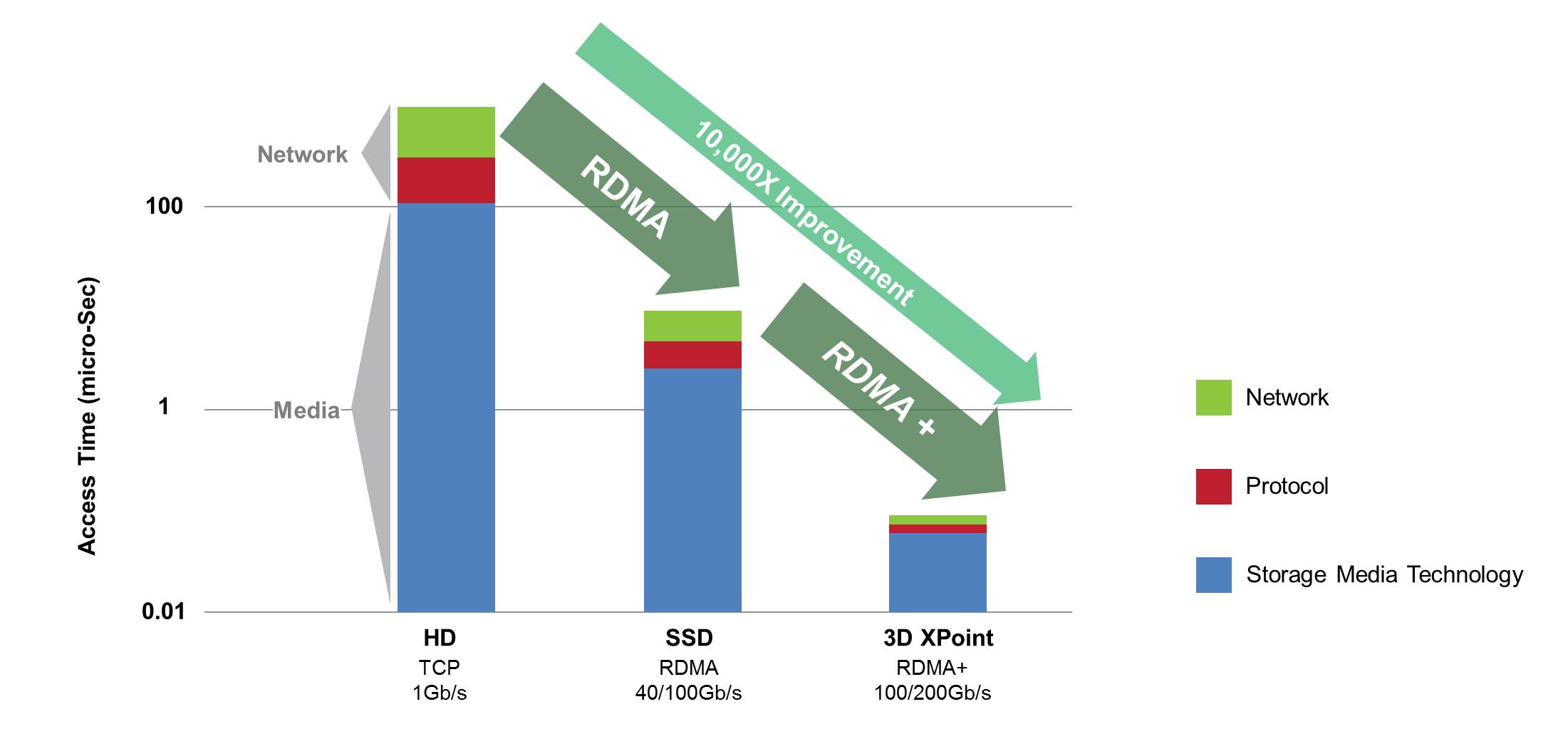
Traditionally, accessing hard disk storage took tens of milliseconds, and the corresponding network and protocol overheads were in the hundreds of microseconds, a negligible percentage of the overall access time.
At that time, networks ran on 1Gb/s bandwidth, and SCSI was the protocol used for accessing storage locally while iSCSI based on TCP was developed for remote access.
However, once storage technology improved and Solid-State Disks (SSD) became the norm, access time dropped by two orders of magnitude to the hundreds of microseconds. Unless network and protocol access times decreased by a similar factor, they would create a bottleneck that negated the gains made by the new media technology.
This meant that the network had to handle larger bandwidths, such as 40Gb/s and now even 100Gb/s driving faster data transfers. For remote access, iSCSI is still the protocol of choice; however, TCP was no longer efficient enough, such that RDMA (RoCE) became the transport of choice for data plane operation and iSER was developed as an enhancement of iSCSI.
SSD access was emulated under the SCSI layer to maintain compatibility to the existing ecosystem of block storage access, but it inherited all the overhead associated with SCSI. Recently, NVMe was invented for more efficient access to flash media, enabling higher concurrency and eliminating SCSI overhead. NVMe over Fabrics is defined as an RDMA-based protocol requiring RDMA as a basic foundation upon which the storage protocols required for advanced storage media technologies are built. RoCE is an industry standard protocol running on Ethernet/IP and InfiniBand networks and is the most efficient RDMA implementation available.
Mellanox is the world’s leader for RDMA solutions, with the most efficient implementation on the market. Mellanox also is the pace-setter for network performance improvements, becoming the first to offer end-to-end 100Gb/s solutions with sub-microsecond latency in 2015.
Now, storage media technology is on the verge of yet another 100-fold performance leap, and concepts such as Intel’s 3D Xpoint technology reinforce the idea that even more efficient networking will be required. Mellanox remains at the forefront of development of the networking roadmap and can be relied upon to provide the most efficient solutions for storage going forward.
This article was submitted by Michael Kagan, Chief Technology Officer and a co-founder of Mellanox Technologies. Michael is responsible for steering Mellanox’s product roadmap.