 The CloudLightning Project in Europe has published preliminary results from a survey on Barriers to Using HPC in the Cloud.
The CloudLightning Project in Europe has published preliminary results from a survey on Barriers to Using HPC in the Cloud.
Cloud computing is transforming the utilization and efficiency of IT infrastructures across all sectors. Historically, cloud computing has not been used for high performance computing (HPC) to the same degree as other use cases for a number of reasons. This executive briefing is a preliminary report of a larger study on demand-side barriers and drivers of cloud computing adoption for HPC. A more comprehensive report and analysis will be published later in 2016. From June to August 2016, the CloudLightning project surveyed over 170 HPC discrete end users worldwide in the academic, commercial and government sectors on their HPC use, perceived drivers and barriers to using cloud computing, and uses of cloud computing for HPC.
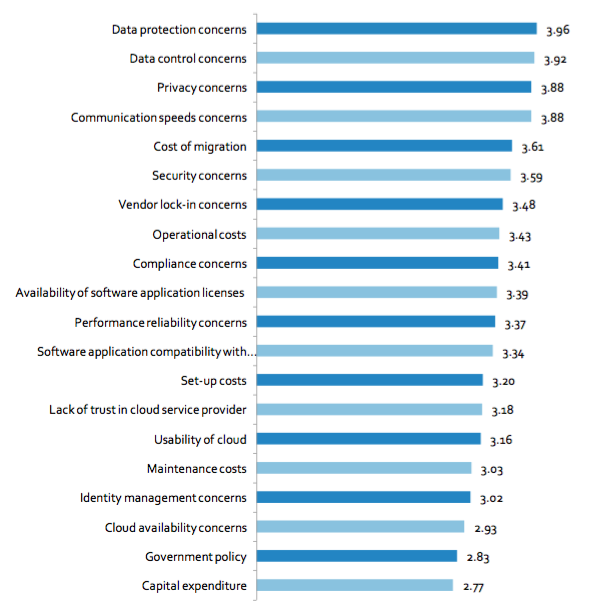
Figure 2. Figure 2 Barriers to cloud computing adoption for HPC workloads (n=92)
As shown in Figure 2, trust in cloud computing would appear to be a significant barrier to adopting cloud computing for HPC workloads. Data management concerns dominate the responses. This is not surprising given the large number of bio-science and university and academic respondents within the sample. The main technical barriers relate to communication speeds. This reflects a perceived lack of cloud infrastructure capable of meeting the communications and I/O requirements of high-end technical computing. Government policy is again ranked low it would seem it is neither a driver nor a barrier. Unsurprisingly availability and capital expenditure are not barriers reflecting their positive impact on adoption.
According to the report, there is unlikely to be a full shift of high performance computing workloads to the cloud in the short term however there is evidence of demand to meet the capacity limitations of internal infrastructures including use cases for testing the viability of the cloud or specific software for various use cases. This is consistent with previous research.
Funded by the European Commission’s Horizon 2020 Program for Research and Innovation, CloudLightning brings together eight project partners from five countries across Europe. The project proposes to create a new way of provisioning heterogeneous cloud resources to deliver services, specified by the user, using a bespoke service description language. Our goal is to address energy inefficiencies particularly in the use of resources and consequently to deliver savings to the cloud provider and the cloud consumer in terms of reduced power consumption and improved service delivery, with hyperscale systems particularly in mind.




