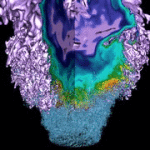
As advances in hardware/software technologies, sensing technologies and math-physics have progressed the ratio of data to compute power has remained relatively constant as the goal is increasing the resolution of the subsurface. The talk will provide the path taken and where it might go in the future in and how it might connect to opportunities in the XLDB arena.
Archives for September 2013
Supercomputing Cleaner Combustion
However, algorithmic improvements developed by scientists and mathematicians in CCSE have slashed computational costs for combustion simulations by a factor of 10,000 while the number of variables used to specify the solution has increased from hundreds of thousands to more than a billion. The increase in complexity (and fidelity) has made laboratory-scale 3D simulations possible for the first time.
A New TACC App for Your Mobile Device
The TACC app offers valuable news and information about supercomputing’s role in society, and helps our users manage their science wherever they go.
HPC People on the Move – September Edition
Lewey Anton tracks who’s moving on up in high performance computing. Here are the latest developments for September, 2013.
Tape Takes Off — Spectra Logic Achieves Year of Record Results
As a consistently profitable company, Spectra Logic posted 16 percent year-over-year revenue growth, led by strong revenue growth of its flagship product, the Enterprise T-Finity tape library.
Swiss Supercomputing – An Update on CSCS, Piz Daint, and PASC
CSCS is upgrading the Piz Daint supercomputer with Kepler GPUs. The 750 Teraflop machine is now able to a run climate simulations over three times faster than on previous systems.
Dell and HP Reveal Mammoth Modular Datacenters at eBay
eBay’s recently unveiled it’s new data center in Utah featuring advanced data center modules from Dell and HP to deploy high-density servers.
Realizing Dreams: Big Data & Computing in Very Large Projects & Companies
Government funding agencies are understandably conservative when funding huge science projects, such as accelerators or telescopes.” They often lock in technology early in a project’s development. Commercial data projects, on the other hand, have much shorter development time scales and often must be able to change to accommodate rapidly changing needs.
UPDATE: Glenn Lockwood Looks at Intel’s Xeon Phi Uptake Measured from Real Users
Despite having over 6,000 Intel Xeon Phi coprocessors, TACC’s Stampede system is seeing extremely low utilization of these coprocessors.
There is No Other Side: Global Warming is Real and We Humans are Contributing
Great computer power also allows scientists to get down to much better resolutions on smaller scales, like predicting regional climates. “Illinois may be becoming more like eastern Texas, more like the Dallas area for example, where most of the summer is above 90 degrees and you have a month of 100 degree days. Well, that’s not Illinois as we know it.” That scenario is for the end of the century and assumes continued heavy use of fossil fuels.