Sponsored Post
Besides solving the open source configuration problem, Intel HPC Orchestrator ensures that users are able to take immediate advantage of the latest advances in HPC hardware technology.
Historically, High Performance Software stacks for clustered computing systems have been constructed through many individual, loosely coordinated open source efforts, which is great until you update a component and find your HPC system no longer works! In addition to the unwanted downtime, the continual effort required to keep all components synchronized and working together properly can be a huge time sink for HPC system administrators.
In an effort to remove that heavy burden so HPC users can focus on more productive tasks, Intel decided to look for a way to create an open, consistent and widespread solution.
The vision for a common HPC ecosystem was established in November 2015 with the announcement of OpenHPC, a global HPC community effort. Formally launched under the Linux Foundation in May 2016, it now boasts 30 member companies focused on the development of a common HPC software stack that helps eliminate incompatibilities while taking full advantage of the latest software and hardware innovations.
Taking the concept a step further, Intel has added value to the OpenHPC stack through advanced testing, coordinated releases, security updates and technical support. The Intel-supported commercial version of OpenHPC is called Intel® HPC Orchestrator, and is an integral element of the Intel® Scalable System Framework. Besides solving the open source configuration problem, Intel HPC Orchestrator ensures that users are able to take immediate advantage of the latest advances in HPC hardware technology, like the Intel® Xeon and Intel® Xeon Phi™ processor families, the Intel® Omni-Path Architecture (Intel® OPA) fabric, and the Intel® Enterprise Edition for Lustre* Software parallel mass storage solution.
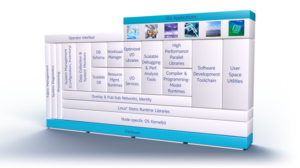
Like OpenHPC on which it is based, Intel HPC Orchestrator is a middleware stack for HPC environments that sits on top of the base operating system and provides everything needed to run a variety of HPC applications from independent software vendors together on the same HPC system. The product includes tools for administration, provisioning, resource and workload management, HPC runtimes, I/O services, scientific libraries, MPI libraries, compilers and other development tools.
To increase system reliability, an automated validation regression test suite is run with the latest OpenHPC and OS releases every time there’s a component change. Performance benchmarks are also run to ensure that changes have not adversely affected system performance. These include the High Performance Conjugate Gradient (HPCG) benchmark, first proposed by Jack Dongarra, and the miniFE benchmark.
Intel HPC Orchestrator has been validated on systems with over 1,000 compute nodes and is designed to support well over 2,000 nodes. Validation is conducted against typical configurations of Intel hardware that an HPC system might use including Intel OPA, the company’s successor to Intel® True Scale Fabric, Lustre file systems and Intel Xeon Phi processors. Such rigorous validation and testing allows Intel to confidently provide Intel HPC Orchestrator customers with full Level 3 technical support across the HPC system software stack. Level 1 and Level 2 support options are also available.
As one of the initiators of the OpenHPC movement, Intel remains heavily involved in the HPC open source community, and has been a longtime supporter of Linux and other open source efforts. Intel contributes to and monitors component updates, integrates them into the latest stack and validates them before adding them to a product release.
Intel HPC Orchestrator also includes a 90-day evaluation license for Intel® Parallel Studio XE 2017, providing a flexible development environment that allows programmers to switch between GCC, GNU and Intel tools, as well as any of the three supported operating systems, and three MPI families (MVAPICH2, OpenMPI, and Intel MPI). Because Intel HPC Orchestrator is a modular system, users can mix and match components. For example, if a developer wants to use the GCC compiler and Intel MPI, an admin can create an Lmod recipe that will automatically load and configure the desired components.
Intel has added value to the OpenHPC stack through advanced testing, coordinated releases, security updates and technical support
Another added value in the Intel HPC Orchestrator product is Intel® Cluster Checker, an analysis tool that’s used for supportability of the entire system. Found within Intel Parallel Studio XE 2017, it enables an admin to record a configuration baseline once a system is completely installed and running correctly. The baseline can then be used to generate an automatic comparison of everything that’s changed in the system since the baseline was created. This shows the support team where things have changed in both hardware and software, down to the version of each program installed. Intel Parallel Studio also helps admins analyze and configure the system for specific workloads to achieve significant increases in performance. In terms of workload managers, Intel HPC Orchestrator now supports SchedMD Slurm and an upcoming release will have full support for Altair PBS Pro.
Intel believes that Intel HPC Orchestrator can save significant time and effort in creating and maintaining an HPC system software stack, enabling end users to not only get better results from the applications they’re working with, but to take full advantage of hardware developments on the path to exascale performance. For application developers, Intel HPC Orchestrator can speed new innovations to market and reduce support costs by providing a known, stable development and runtime environment. Organizations can focus more of their resources on the things that differentiate their products and better meet the needs of their customers.




