Gary Grider, left, and Brad Settlemyer discuss the new Los Alamos and Carnegie Mellon software product, DeltaFS, released to the software distribution site GitHub this week. Source: LANL
A new distributed file system for HPC being distributed today via GitHub provides unprecedented performance for creating, updating and managing extreme numbers of files.
We designed DeltaFS to enable the creation of trillions of files,” said Brad Settlemyer, a Los Alamos computer scientist and project leader. Los Alamos National Laboratory and Carnegie Mellon University jointly developed Delta FS. “Such a tool aids researchers in solving classical problems in high-performance computing, such as particle trajectory tracking or vortex detection.”
DeltaFS builds a file system that appears to the user just like any other file system, doesn’t require specialized hardware, and is exactly tailored to assisting the scientist in new discoveries when using a high-performance computing platform.
One of the foremost challenges, and primary goals of DeltaFS, was scaling across thousands of servers without requiring a portion of them be dedicated to the file system,” said George Amvrosiadis, assistant research professor at Carnegie Mellon University and a coauthor on the project. “This frees administrators from having to decide how to allocate resources for the file system, which will become a necessity when exascale machines become a reality.”
The file system brings about two important changes in high-performance computing. First, DeltaFS enables new strategies for designing the supercomputers themselves, dramatically changing the cost of creating and managing files. In addition, DeltaFS radically improves the performance of highly selective queries, dramatically reducing time to scientific discovery.
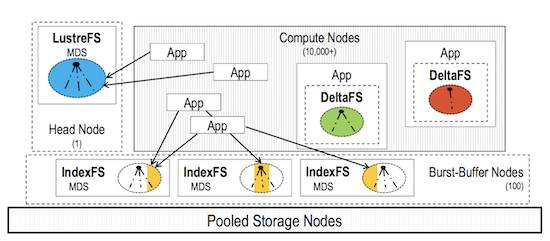
A typical HPC cluster consisting of compute, storage, head, and burst-buffer nodes under different system models: centralized LustreFS server, partitioned IndexFS servers, or fully decentralized DeltaFS. While Lustre and IndexFS requires dedicated metadata servers, DeltaFS allows each application to instantiate a private namespace on compute nodes and self-manage its metadata on storage nodes.
DeltaFS is a transient, software-defined service that allows data to be accessed from a handful up to hundreds of thousands of computers based on the user’s performance requirements.
The storage techniques used in DeltaFS are applicable in many scientific domains, but we believe that by alleviating the metadata bottleneck we have really shown a way for designing and procuring much more efficient HPC storage systems,” Settlemyer said.
Download the paper: DeltaFS: Exascale File Systems Scale Better Without Dedicated Servers




