The Corona cluster is comprised of AMD EPYC processors, AMD Radeon Instinct GPUs connected with Mellanox HDR 200 Gigabit InfiniBand.
Penguin Computing has upgraded the Corona supercomputer at LLNL with the newest AMD Radeon Instinct MI60 accelerators. Based on the Vega 7nm architecture, this upgrade is the latest example of Penguin Computing and LLNL’s ongoing collaboration aimed at providing additional capabilities to the LLNL user community.
The Penguin Computing DOE team continues our collaborative venture with our vendor partners AMD and Mellanox to ensure the Livermore Corona GPU enhancements expand the capabilities to continue their mission outreach within various machine learning communities,” said Ken Gudenrath, Director of Federal Systems at Penguin Computing.
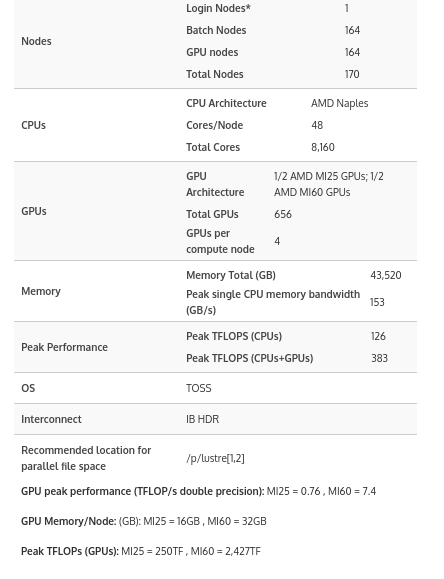
As previously released, the cluster consists of 170 two-socket nodes with 24-core AMD EPYC 7401 processors and a PCIe 1.6 Terabyte (TB) nonvolatile SSDs. Each Corona compute node is GPU-ready with half of those nodes today utilizing four AMD Radeon Instinct MI25 accelerators per node, delivering 4.2 petaFLOPS of FP32 peak performance. With the MI60 upgrade, the cluster increases its potential PFLOPS peak performance to 9.45 petaFLOPS of FP32 peak performance. This brings significantly greater performance and AI capabilities to the research communities.
Corona is being made available to industry through LLNL’s High Performance Computing Innovation Center (HPCIC). Funded through the Commodity Technology Systems (CTS-1) contract with the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), the upgrade will help LLNL researchers and their industry partners improve capabilities in scalable deep learning, big data analytics and data science, while enhancing NNSA’s ability to assess future architectures and meet the needs of the NNSA’s Advanced Simulation & Computing program. It will also provide a higher level of performance for researching cognitive computing and developing predictive simulations for applications such as inertial confinement fusion and molecular dynamics simulations for precision medicine.
This upgrade significantly increases the capability available on Corona,” said Bronis R. de Supinski, Chief Technical Officer for Livermore Computing. “The new Vega GPUs offer substantial double-precision performance, in addition to much more single-precision performance. LLNL scientists will use the combination to understand the potential of mixed-precision algorithms for a variety of domains.”
AMD’s Radeon Instinct MI60 accelerators bring many new features that improve performance, including the Vega 7nm GPU architecture and the AMD Infinity FabricTM Link technology, a peer-to-peer GPU communications technology that delivers up to 184 GB/s transfer speeds between GPUs – which is 5.75X faster than PCIe Gen 3, and full-chip Error-correcting code (ECC)11 and Reliability, Accessibility and Serviceability (RAS) 12 technologies. The new accelerators also utilize the latest ROCm open source software stack, which is now integrated into leading frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch and maps workloads to the heterogeneous compute resources of the underlying hardware.
AMD is pleased to continue collaboration with LLNL and the NNSA in advancing open accelerator solutions. Access to systems like Corona enable next generation scientific discovery as we move to the exascale era,” said Ogi Brkic, Corporate Vice President and General Manager of the Data Center GPU Business Unit at AMD.