A new whitepaper from NEC X delves into the world of unstructured data and explores how vector processors and their optimization software can help solve the challenges of wrangling the ever-growing volumes of data generated globally. “In short, vector processing with SX-Aurora TSUBASA will play a key role in changing the way big data is handled while stripping away the barriers to achieving even higher performance in the future.”
Bright Cluster Manager for Data Science Now Available at No Charge with Easy8
Today Bright Computing announced that Bright Cluster Manager for Data Science is now available at no charge as part of the Easy8 program. Launched in November of 2019, Easy8 is designed to put Bright’s award-winning cluster management software in the hands of every organization working with high-performance Linux clusters. Easy8 offers the full-featured Bright Cluster Manager software free for up to 8 nodes, and now includes Bright Cluster Manager for Data Science. Bright Cluster Manager automates the process of building and managing heterogeneous Linux clusters that span from your on-premise datacenter to the cloud, and to the edge.
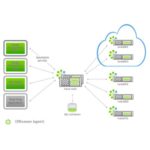
The GigaIO FabreX Network – New Frontiers in Networking For Big Data
GigaIO has developed a new whitepaper to describe GigaIO FabreX, a fundamentally new network architecture that integrates computing, storage, and other communication I/O into a single-system cluster network, using industry standard PCIe (peripheral component interconnect express) technology.
The GigaIO™ FabreX™ Network – New Frontiers in Networking For Big Data
In order to derive meaning from big data, via implementing the capabilities of big data analytics, and create new opportunities and new value, organizations must find a way to obtain radically increased overall system throughput. This whitepaper describes how the GigaIO FabreX network makes such accelerated functionalities possible by achieving exceptionally low latency and high-bandwidth performance across an organization’s entire network.
Video: The Convergence of Big Data and Large-scale Simulation
David Keyes from KAUST gave this talk at ATPESC 2019. “Analytics can provide to machine learning feature vectors for training. Machine learning, in turn, can impute missing data and provide detection and classification. The scientific opportunities are potentially enormous enough to overcome the inertia of the specialized communities that have gathered around each of paradigms and spur convergence.”
Atos Launches Quantum Learning Machine User Group
Today Atos launched the global User Group of the Atos Quantum Learning Machine (QLM). Chaired by a representative from French multi-national energy company Total, the User Group ecosystem is supported by the Atos’ Quantum Scientific Council, which includes universally recognized quantum physicists. It is also further enhanced by partners such as leading software company Zapata and start-up Xofia. “Now, with the creation of this Group of Atos QLM Users, we are ensuring that we continue to support them to develop new advances in deep learning, algorithmics and artificial intelligence with the support of the breakthrough computing acceleration capacities that quantum simulation provides.”
Building a Tiered Digital Storage Environment Based on User-Defined Metadata to Enable eResearch
In this special guest feature, David Fellinger from the iRODS Consortium writes that, as eResearch has evolved to accommodate sensor and other types of big data, iRODS can enable complete workflow control, data lifecycle management, and present discoverable data sets with assured traceability and reproducibility.