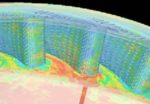
Today Microsoft announced general availability of Azure HBv2-series Virtual Machines designed to deliver leadership-class performance, message passing interface (MPI) scalability, and cost efficiency for a variety of real-world HPC workloads. “HBv2 VMs deliver supercomputer-class performance, message passing interface (MPI) scalability, and cost efficiency for a variety of real-world high performance computing (HPC) workloads, such as CFD, explicit finite element analysis, seismic processing, reservoir modeling, rendering, and weather simulation. Azure HBv2 VMs are the first in the public cloud to feature 200 gigabit per second HDR InfiniBand from Mellanox.
GE Research Leverages World’s Top Supercomputer to Boost Jet Engine Efficiency
GE Research has been awarded access to the world’s #1-ranked supercomputer to discover new ways to optimize the efficiency of jet engines and power generation equipment. Michal Osusky, the project’s leader from GE Research’s Thermosciences group, says access to the supercomputer and support team at OLCF will greatly accelerate learning insights for turbomachinery design improvements that lead to more efficient jet engines and power generation assets, stating, “We’re able to conduct experiments at unprecedented levels of speed, depth and specificity that allow us to perceive previously unobservable phenomena in how complex industrial systems operate. Through these studies, we hope to innovate new designs that enable us to propel the state of the art in turbomachinery efficiency and performance.”
Video: Making Supernovae with Jets
Chelsea Harris from the University of Michigan gave this talk at the CSGF 2019. “I am developing a FLASH hydrodynamics module, SparkJoy, to perform these simulations at high order. These projects are part of a DOE INCITE project to explore progenitor effects on CC SNe and of the DOE SciDAC program “Towards Exascale Astrophysics of Mergers and Supernovae.”
Reducing the risk of blood clots by supercomputing turbulent flow
People with mechanical heart valves need blood thinners on a daily basis, because they have a higher risk of blood clots and stroke. With the help of the Piz Daint supercomputer, researchers at the University of Bern have identified the root cause of blood turbulence leading to clotting. Design optimization could greatly reduce the risk of clotting and enable these patients to live without life-long medication.
Predictive Data Science for Physical Systems: From Model Reduction to Scientific Machine Learning
Karen Willcox from the University of Texas gave this Invited Talk at SC19. “This talk highlights how physics-based models and data together unlock predictive modeling approaches through two examples: first, building a Digital Twin for structural health monitoring of an unmanned aerial vehicle, and second, learning low-dimensional models to speed up computational simulations for design of next-generation rocket engines.”
CFD Leader NUMECA adopts Advania Data Centers for HPC-as-a-Service
Today Advania Data Centers (ADC) announced a strategic HPC service partnership with NUMECA International, a market leader in computational fluid dynamics CFD, multiphysics and optimization. “This HPCaaS partnership allows NUMECA to concentrate on its core software developments and support activities while ADC handles its HPC cluster management, power and cooling — ensuring peak performance at all times based on their Intel Xeon Scalable processor-based infrastructure.”
Video: Large scale industrial simulations using HPC at Rolls-Royce
Leigh Lapworth from Rolls-Royce gave this talk at m Computing Systems Week Edinburgh 2019. “Simulation and modeling, enabled by high performance computing, have transformed the way Rolls-Royce designs and engineers its products. Every advance in computing power unlocks the power to do more with simulation and modeling whether this is larger models to give higher fidelity; or, higher throughput of models to explore a larger part of the design space.”
Podcast: Univa Speeds CFD with SportPesa Racing Point F1 Team
In a sport that hangs in the complex balance of speed, aerodynamics and the ever-present data, SportPesa Racing Point deserves the best from its computation, which is capped at 25 teraflops. For SportPesa Racing Point, the best is Univa Grid Engine, which manages its CFD cluster up into the 97 percent range at a sustained level. “Univa help us with bringing developments and CFD developments to reality faster. So they help with efficiency with our compute power.”
Simulating Shock Turbulence Interactions on Stampede II
In this special guest feature, Jorge Salazar from TACC writes that Researchers are using XSEDE supercomputers to better understand shock turbulence interactions. “We proposed that, instead of treating the shock as a discontinuity, one needs to account for its finite thickness as in real life which may be involved as a governing parameter in, for example, amplification factors,” Donzis said.
Video: HPC for Instabilities in Aerospace Propulsion Systems
Thierry Poinsot from Toulouse Fluid Mechanics Institute gave this talk at PASC19. “This talk focuses on aerospace propulsion where optimization often leads to the occurrence of instabilities where combustion couples with acoustics, leading to unacceptable oscillations (the most famous example is the Apollo engine which required 1330 full scale tests to reach acceptable oscillation levels). The talk will show how simulation is used to control these problems, in real gas turbine engines and in rocket engines.”