In this video from the HPC User Forum in Tucson, Miyoshi Takemasa from RIKEN presents: Big Data Assimilation Revolutionizing Weather Prediction. “A new project harnessing data from a Japanese satellite called Himawari-8 could improve weather forecasting and allow officials to issue life-saving warnings before natural disasters. The breakthrough is the result of pairing data collected by Japan’s Himawari-8 weather satellite with a program run on a supercomputer at the RIKEN science institute.”
Video: Japan’s Post K Computer
Yutaka Ishikawa from Riken AICS presented this talk at the HPC User Forum. “Slated for delivery sometime around 2022, the ARM-based Post-K Computer has a performance target of being 100 times faster than the original K computer within a power envelope that will only be 3-4 times that of its predecessor. RIKEN AICS has been appointed as the main organization for leading the development of the Post-K.”
Post K Supercomputer Delayed in Japan
Nikkei in Japan writes that the Post K supercomputer is facing 1-2 year delay for deployment as part of the Flagship2020 project. Originally targeted for completion in 2020, the ARM-based Post K supercomputer has a performance target of being 100 times faster than the original K computer within a power envelope that will only be 3-4 times that of its predecessor. Nikkei cites semiconductor development issues as the reason for the project delay.
Video: System Software in Post K Supercomputer
“The next flagship supercomputer in Japan, replacement of K supercomputer, is being designed toward general operation in 2020. Compute nodes, based on a manycore architecture, connected by a 6-D mesh/torus network is considered. A three level hierarchical storage system is taken into account. A heterogeneous operating system, Linux and a light-weight kernel, is designed to build suitable environments for applications. It can not be possible without codesign of applications that the system software is designed to make maximum utilization of compute and storage resources. “
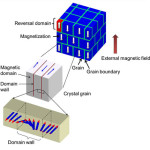
K Computer Runs World’s Largest-Scale Magnetic-Reversal Simulator
Today Fujitsu Limited announced it has developed the world’s largest magnetic-reversal simulator. Developed in joint research with the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), the simulator runs on the famous K computer using a mesh covering more than 300 million micro-regions. Based on the large-scale magnetic-reversal simulation technology first developed in 2013, this new development offers a faster calculation algorithm and more efficient massive parallel processing.