This insideHPC guide explores networking with Dell EMC Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes.

Download the full report.
Dell EMC Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes are built on Dell EMC PowerEdge servers, which provide the storage density and compute power to maximize the benefits of Storage Spaces Direct (S2D). They leverage the advanced feature sets in Windows Server 2016 Datacenter Edition to deploy a scalable hyper-converged infrastructure solution with Hyper-V and Storage Spaces Direct. For Microsoft server environments, S2D scales to 16 nodes in a cluster, and is a kernel-loadable module, (with no RDMA iWarp or RoCE needed) which is a low risk approach to implementing an S2D cluster. Dell EMC Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes can be ordered with software installed with or as bare metal for customers with volume license agreements.
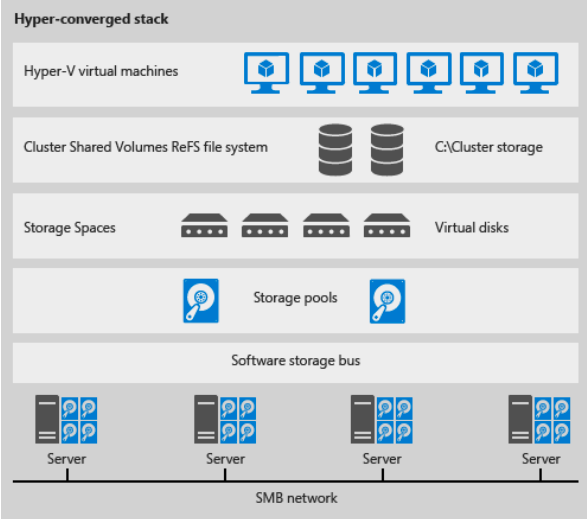
Hyper-V VMs run directly on the Storage Spaces Direct cluster that hosts the storage, as shown. Virtual machine files are stored on local CSVs. This allows for scaling Hyper-V compute clusters together with the storage
it is using, reducing the number of clusters required. See Deploying Storage Spaces Direct from Microsoft, and see Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes – Sample Switch Configurations.
You can use Windows Server 2016 Datacenter Edition with the Server Core, or Server with Desktop Experience installation options, the steps in the “Configure the Network” and “Configure Storage Spaces Direct” sections are identical whether you are using Server with Desktop Experience or Server Core installations. The management system can be run inside of a virtual machine or on a physical machine, however, the management system needs to be joined to the same domain or a fully trusted domain. There are several deployment options available to connect the cluster nodes, and RDMA is not available for networking inside a virtual machine.
Storage Spaces Direct requires high bandwidth and low latency network connections between nodes. This network connectivity is important for both system performance and reliability. When using physical nodes instead of VMs, using at least two 10 Gb connections between the nodes is recommended, preferably with RDMA to increase throughput and reduce the CPU usage for network traffic.
The disks intended for Storage Spaces Direct need to be empty and without partitions or other data. If a disk has partitions or other data, it will not be included in the Storage Spaces Direct system.
There are two common versions of remote direct memory access (RDMA) network adapters — RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) and Internet Wide-area RDMA Protocol (iWARP). You can use either with Storage Spaces Direct as long as it has the Windows Server 2016 logo, but iWARP usually requires less configuration.

Top of Rack switches and server configurations vary depending on the network adapters and switches. Configuring the server and switch correctly is important to ensure reliability and performance of Storage Spaces Direct.
Ensure that there is no data on any of the disks of the cluster before running configuration commands or scripts. It will remove any data on the disks that are not being used by the operating system.
Windows Server 2016 also introduces a new virtual switch that has network teaming built in called Switch Embedded Teaming (SET). This virtual switch allows the same physical NIC ports to be used for all network traffic while using RDMA. This reduces the number of physical NIC ports that would otherwise be required and allows network management through the Software Defined Network features of Windows Server.
If you’re deploying a hyper-converged cluster, the last step is to provision virtual machines on the Storage Spaces Direct cluster.
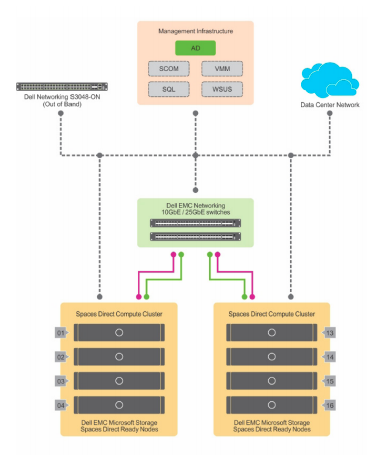
After deploying your clustered file server, we recommend testing the performance of your solution using test workloads before bringing up any production workloads. This lets you confirm that the solution is performing properly and work out any lingering issues before adding the complexity of production workloads. For more info, see Test Storage Spaces Performance Using Synthetic Workloads.
This insideHPC guide series will also cover the following topics in the coming weeks:
- How Do I Network vSAN Ready Nodes?
- Exploring Dell EMC Networking for vSan
- Network switch configuration with Dell EMC Ready Nodes
- Where Ready Nodes are the optimal choice
Download the full report, “A Practical Guide to Networking Dell EMC Ready Nodes,” courtesy of Dell EMC, to learn more about Dell EMC Ready Nodes and Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes.



