 Today NVIDIA made a number of announcements centered around Machine Learning software at the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference in Salt Lake City.
Today NVIDIA made a number of announcements centered around Machine Learning software at the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference in Salt Lake City.
NVIDIA is kicking off the conference by demonstrating an early release of Apex, an open-source PyTorch extension that helps users maximize deep learning training performance on NVIDIA Volta GPUs. Inspired by state of the art mixed precision training in translational networks, sentiment analysis, and image classification, NVIDIA PyTorch developers have created tools bringing these methods to all levels of PyTorch users. Mixed precision utilities in Apex are designed to improve training speed while maintaining the accuracy and stability of training in single precision. Specifically, Apex offers automatic execution of operations in either FP16 or FP32, automatic handling of master parameter conversion, and automatic loss scaling, all available with 4 or fewer line changes to the existing code. Learn more.
Other announcements include:
- NVIDIA DALI (Data Loading LIbrary) is an open source library researchers can use to accelerate data pipelines by 15% or more. By accelerating data augmentations using GPUs, NVIDIA DALI addresses performance bottlenecks in today’s computer vision deep learning applications that include complex, multi-stage data augmentation steps. With DALI, deep learning researchers can scale training performance on image classification models such as ResNet-50 with MXNet, TensorFlow , and PyTorch across Amazon Web Services P3 8 GPU instances or DGX-1 systems with Volta GPUs. Framework users will have lesser code duplication due to consistent high-performance data loading and augmentation across frameworks. To demonstrate its power, NVIDIA data scientists used it to fine-tune DGX-2 to achieve a record-breaking 15,000 images per second in training. Now, it’s available to all. Learn more.
- NVIDIA TensorRT 4 programmable inference accelerator is now generally available. TensorRT 4 speeds up deep learning inference applications such as neural machine translation, recommender systems, speech and image processing applications on GPUs. NVIDIA has measured speedups of 45x to 190x across these application areas. TensorRT 4 is available as a free download to all members of the NVIDIA Registered Developer Program from the TensorRT product page. Learn more.
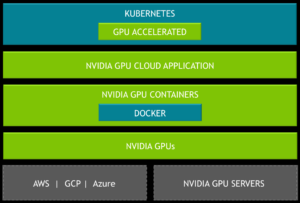
- Kubernetes on NVIDIA GPUs, which facilitates enterprise inference deployment on multi-cloud GPU clusters, is now openly available to the research community on GitHub. Kubernetes on NVIDIA GPUs enables enterprises to scale up training and inference deployment to multi-cloud GPU clusters seamlessly. It lets you automate the deployment, maintenance, scheduling and operation of multiple GPU accelerated application containers across clusters of nodes. With increasing number of AI powered applications and services and the broad availability of GPUs in public cloud, there is a need for open-source Kubernetes to be GPU-aware. With Kubernetes on NVIDIA GPUs, software developers and DevOps engineers can build and deploy GPU-accelerated deep learning training or inference applications to heterogeneous GPU clusters at scale, seamlessly. Learn more.
In this video, Virag Chavan from NVIDIA presents: The Path to GPU as a Service in Kubernetes.



