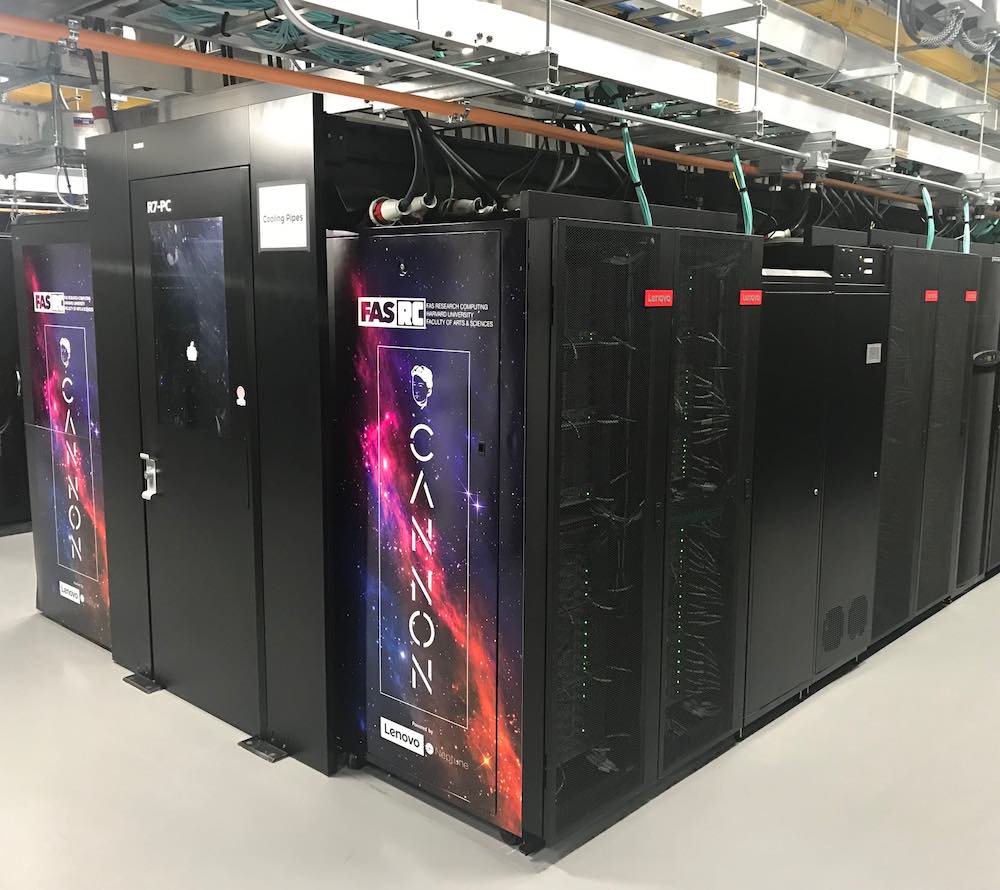
Today Lenovo announced the deployment of Cannon, Harvard University’s first liquid-Cooled supercomputer. Developed in cooperation with Intel, the new system’s advanced supercomputing infrastructure will enable discoveries into areas such earthquake forecasting, predicting the spread of disease, and star formation.
Today Lenovo announced the deployment of Cannon, Harvard University’s first liquid-Cooled supercomputer. Developed in cooperation with Intel, the new system’s advanced supercomputing infrastructure will enable discoveries into areas such earthquake forecasting, predicting the spread of disease, and star formation.
Cannon performs 3-4x faster than its predecessor with the upgrade to Lenovo’s ThinkSystem SD650 NeXtScale servers, Neptune liquid cooling, and 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Platinum 8268 processors.
Leveraging Lenovo and Intel’s long-standing collaboration to advance HPC and artificial intelligence (AI) in the data center, FASRC sought to refresh its previous cluster, Odyssey. Harvard’s Faculty of Arts and Sciences Research Computing unit (FASRC) wanted to keep the processor count high and increase the performance of each individual processor, knowing that 25 percent of all calculations are run on a single core. Liquid cooling is paramount to support the increased levels of performance today, and the extra capacity needed to scale in the future.
Cannon, comprised of more than 30,000 2nd gen Intel Xeon Scalable processor cores, includes Lenovo’s Neptune liquid cooling technology, which uses the superior heat conducting efficiency of water versus air. Now, critical server components can operate at lower temperatures allowing for greater performance and energy savings. The dramatically enhanced performance enabled by the new system reflects Lenovo’s focus of bringing exascale level technologies to a broad universe of users everywhere – what Lenovo has coined “From Exascale to Everyscale.”
Though the Cannon storage system is spread across multiple locations, the primary compute is housed in the Massachusetts Green High Performance Computing Center, a LEED Platinum-certified data center in Holyoke, MA. The Cannon cluster includes 670 Lenovo ThinkSystem SD650 NeXtScale servers featuring direct-to-node water-cooling, and Intel Xeon Platinum 8268 processors consisting of 24 cores per socket and 48 cores per node. Each Cannon node is now several times faster than any previous cluster node, with jobs like geophysics models of the Earth performing 3-4 times faster than the previous system. In the first four weeks of production operation, Cannon completed over 4.2 million jobs utilizing over 21 million CPU hours.
Science is all about iteration and repeatability. But iteration is a luxury that is not always possible in the field of university research because you are often working against the clock to meet a deadline,” said Scott Yockel, director of research computing at Harvard University’s Faculty of Arts and Sciences. “With the increased compute performance and faster processing of the Cannon cluster, our researchers now have the opportunity to try something in their data experiment, fail, and try again. Allowing failure to be an option makes our researchers more competitive.”
The additional cores and enhanced performance of the system are also attracting researchers from additional departments at the university, such as Psychology and the School of Public Health, to more frequently leverage its machine learning capabilities to speed and improve their discoveries.
Lenovo Launches Exascale Visionary Council
In related news, Lenovo and Intel announced the creation of an exascale visionary council called Project Everyscale. The project mission is to enable broad adoption of exascale-focused technologies for organizations of all sizes.
Project Everyscale, will address the range of component technologies being developed to make exascale computing possible. Areas of focus will touch all aspects of the design of HPC systems, including everything from alternative cooling technologies to efficiency, density, racks, storage, the convergence of traditional HPC and AI and more. The visionaries on the council will bring to bear their insights as customers to set the direction for exascale innovation that everyone can use, working together to bring to life a cohesive picture of the future for the industry.
Working with Intel, we are now bringing together some of the biggest names and brightest minds of HPC to develop an innovation roadmap that will push the design and dissemination of exascale technologies to users of all sizes,” said Scott Tease, general manager for HPC and AI, Lenovo Data Center Group.
Member organizations are leading the way on groundbreaking research into some of the world’s greatest challenges in fields such as computational chemistry, geospatial analysis, astronomy, climate change, healthcare, and meteorology.
Intel is proud to be an integral part of this important endeavor in supercomputing along with Lenovo and other leaders in HPC,” said Trish Damkroger, vice president and general manager of the Extreme Computing Organization at Intel. “With Project Everyscale, our goal is to democratize exascale technologies and bring leading Xeon scalable processors, accelerators, storage, fabrics, software and more to HPC customers of every scale or any workload.”
The Council is slated to kick-off its work early in 2020.