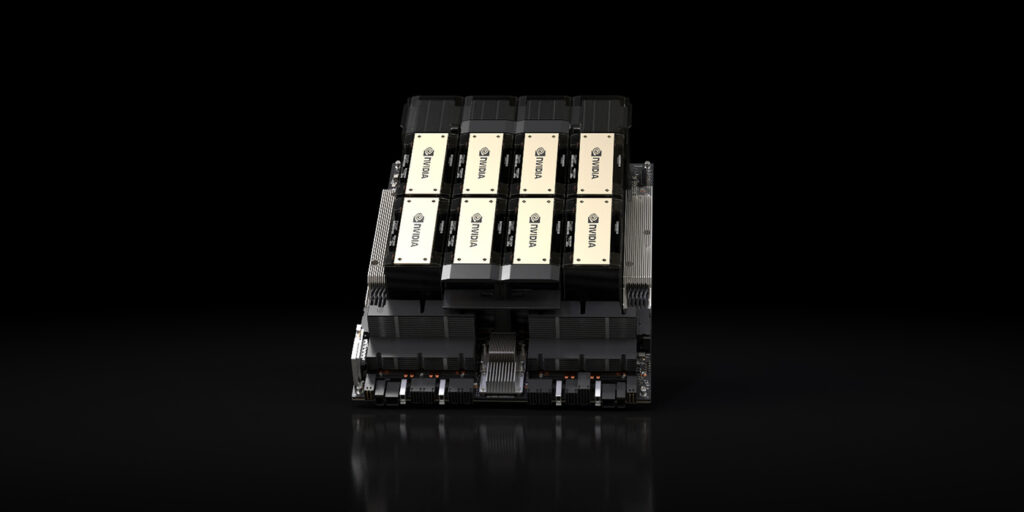
DENVER—SC23—Nov. 13, 2023—NVIDIA today announced the HGX H200 that is based on the Hopper architecture and features the H200 Tensor Core GPU with advanced memory to handle massive amounts of data for generative AI and high performance computing workloads.
NVIDIA said the H200 is the first GPU to offer HBM3e — faster, larger memory to fuel the acceleration of genAI and large language models, while advancing scientific computing for HPC workloads. With HBM3e, the NVIDIA H200 delivers 141GB of memory at 4.8 terabytes per second, nearly double the capacity and 2.4x more bandwidth compared with its predecessor, the NVIDIA A100.
H200-powered systems from server manufacturers and cloud service providers are expected to begin shipping in the second quarter of 2024.
“To create intelligence with generative AI and HPC applications, vast amounts of data must be efficiently processed at high speed using large, fast GPU memory,” said Ian Buck, vice president of hyperscale and HPC at NVIDIA. “With NVIDIA H200, the industry’s leading end-to-end AI supercomputing platform just got faster to solve some of the world’s most important challenges.”
The company said the NVIDIA Hopper architecture delivers a performance leap over its predecessor and benefits from ongoing software enhancements with H100, including the recent release of powerful open-source libraries like NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM.
 The introduction of H200 will lead to performance improvements, including nearly doubling inference speed on Llama 2, a 70 billion-parameter LLM, compared to the H100. Additional performance leadership and improvements with H200 are expected with future software updates, according to NVIDIA.
The introduction of H200 will lead to performance improvements, including nearly doubling inference speed on Llama 2, a 70 billion-parameter LLM, compared to the H100. Additional performance leadership and improvements with H200 are expected with future software updates, according to NVIDIA.
NVIDIA H200 will be available in NVIDIA HGX H200 server boards with four- and eight-way configurations, which are compatible with both the hardware and software of HGX H100 systems. It is also available in the NVIDIA GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip with HBM3e, announced in August.
With these options, H200 can be deployed in various types of data center, including on premises, cloud, hybrid-cloud and edge. NVIDIA’s global ecosystem of partner server makers — including ASRock Rack, ASUS, Dell Technologies, Eviden, GIGABYTE, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Ingrasys, Lenovo, QCT, Supermicro, Wistron and Wiwynn — can update their existing systems with an H200.
Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure will be among the first cloud service providers to deploy H200-based instances starting next year, in addition to CoreWeave, Lambda and Vultr.
Powered by NVIDIA NVLink and NVSwitch high-speed interconnects, HGX H200 is bukilt for various application workloads, including LLM training and inference for the largest models beyond 175 billion parameters.
An eight-way HGX H200 provides over 32 petaflops of FP8 deep learning compute and 1.1TB of aggregate high-bandwidth memory for the highest performance in generative AI and HPC applications.
When paired with NVIDIA Grace CPUs with an ultra-fast NVLink-C2C interconnect, the H200 creates the GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip with HBM3e — an integrated module designed to serve giant-scale HPC and AI applications.
NVIDIA’s accelerated computing platform is supported by software tools that enable developers and enterprises to build and accelerate production-ready applications from AI to HPC. This includes the NVIDIA AI Enterprise suite of software for workloads such as speech, recommender systems and hyperscale inference.
The NVIDIA H200 will be available from global system manufacturers and cloud service providers starting in the second quarter of 2024.
Watch Buck’s SC23 special address on Nov. 13 at 6 a.m. PT to learn more about the NVIDIA H200 Tensor Core GPU.