The following special feature appears in the Print ‘n Fly Guide to SC14 in New Orleans, a downloadable in-flight magazine custom tailored for your journey to the Big Easy at SC14.
The oil and gas industry is one of the heavyweights in the world of high performance computing, especially when it comes to exploration based on seismic processing and imaging. The demand for constantly increasing amounts of data in shorter periods of time has companies like DownUnder GeoSolutions (DUG) continuously upgrading their IT infrastructure to meet their customers’ needs. Billions of dollars are at stake.
DUG is a global geosciences company based in Perth, Australia that offers seismic processing and interpretation solutions to the oil and gas industry. The company takes an integrated approach across a comprehensive line-up of service offerings that includes: seismic acquisition design and implementation; seismic data processing; depth imaging; petrophysical processing and interpretation; quantitative interpretation services; geostatistical depth conversion; and a complete range of DUG domain-specific software.
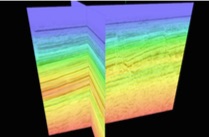 In order to provide its customers with the critical data and insights they need to be successful in a highly competitive industry, DUG is deeply involved in the world of HPC. Among the compute-intensive jobs that the company runs on a daily basis are: Kirchhoff pre-stack time migration, pre-stack depth migration and reverse time migration (RTM), a powerful set of techniques for imaging geologic structures. Other staples include Radon demultiple and 3D SRME for removing coherent noise in the data. Recently DUG began working with full waveform inversion (FWI) for creating high resolution velocity models, a discipline that adds to the company’s HPC burden. Depending on the amount and complexity of the datasets, these compute-intensive jobs – such as RTM – could take days to months to run on DUG’s previous IT infrastructure.
In order to provide its customers with the critical data and insights they need to be successful in a highly competitive industry, DUG is deeply involved in the world of HPC. Among the compute-intensive jobs that the company runs on a daily basis are: Kirchhoff pre-stack time migration, pre-stack depth migration and reverse time migration (RTM), a powerful set of techniques for imaging geologic structures. Other staples include Radon demultiple and 3D SRME for removing coherent noise in the data. Recently DUG began working with full waveform inversion (FWI) for creating high resolution velocity models, a discipline that adds to the company’s HPC burden. Depending on the amount and complexity of the datasets, these compute-intensive jobs – such as RTM – could take days to months to run on DUG’s previous IT infrastructure.
DUG was already using highly-parallel processing codes that were well-tuned to successive generations of multi-threaded CPUs. The use of explicit threading and SSE code (Intel® Streaming SIMD Extensions technology used to enhance the performance of floating-point operations) had already taken the performance of its current IT systems to its limit.
It was obvious that we needed a hardware upgrade, so we went looking for a cost effective solution from both an environmental and hardware perspective,” says Dr. Matt Lamont, DUG’s Managing Director.
Specifically DUG’s IT organization needed an upgrade that would provide outstanding ROI and TCO, while, at the same time, facilitate code porting and optimize the effectiveness of the system’s coprocessors across a wide range of algorithms, such as RTM and FWI.
Seeking a Solution with SGI and Intel
DUG already had a decade’s worth of experience working with SGI and Intel, and turned to those two companies for a solution. The SGI customized solution based on its SGI Rackable HPC environment, powered by Intel Xeon processors and Intel Xeon Phi coprocessors, handily met all of DUG’s requirements for processing its constantly growing influx of seismic data.
The customized SGI Rackable environment deployed by DUG includes 3,800 Intel Xeon Phi coprocessors, making it one of the largest commercial deployments of Intel’s advanced solution.
The custom-built, high performance Rackables feature dual socket Intel Xeon E5-2660 v2 processors coupled with four Intel Xeon Phi 7120 coprocessors. Included are 16GB of onboard memory per Intel Xeon Phi and 128GB of system memory. Local scratch storage is provided by 800GB SSD and each custom solution is connected by a 10GB non-blocking network.
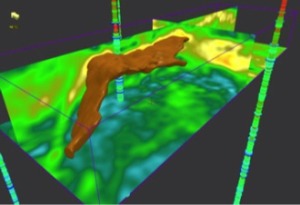 The company has a number of applications – including the workhorse Kirchhoff time-migration algorithm – running up to 1,000-way thread parallelism per compute node with large jobs distributed across hundreds of cluster nodes.
The company has a number of applications – including the workhorse Kirchhoff time-migration algorithm – running up to 1,000-way thread parallelism per compute node with large jobs distributed across hundreds of cluster nodes.
Within a single compute node, adaptive load-balancing across multiple Intel Xeon Phi’s achieves linear speedups. Depending on the application, each Intel Xeon Phi delivers between 1.5 and 2 times the performance of the high-end hosts (which typically have 2 x 10-core Intel Xeon E5-2660 v2 processors).
Use of the Intel Xeon Phi coprocessors has allowed DUG to quickly adapt its existing code and pass this value on to its customers. Overall, the new environment provides DUG with an added compute capacity of roughly six peak petaflops.
Benefits of DUG’s Advanced Technology
DUG reports that the Intel Xeon Phi architecture offers a number of advantages as a “co-processor” scale up. These include:
- Most of the classical HPC optimization techniques used in DUG software still apply. The benefits of many of these techniques are amplified on the Intel Xeon Phi because of the scale of the processor.
- The plethora of existing sophisticated library infrastructure (such as pthreads, queues, work pools, and LRU caches) expressed in a standard language require virtually no change to function and perform well on the Intel Xeon Phi.
- The integrated compiler support and execution model means that the deployment is reasonably transparent to the end-user processing staff.
We have already started to see dramatic improvements in turn-around times when we compare our upgraded machines to those without coprocessors,” says Lamont. “Our time migration now runs more than 10 times faster, and our depth migration runs six times faster. Reverse time migration (RTM) also runs significantly faster on this new technology.”
The upgraded system is allowing DUG to turn its seismic processing work around much more quickly and, as a result, conduct more tests for its clients.
“By combining the Intel Xeon Phi coprocessors with our proprietary software, DUG Insight, we are able to provide our customers with one of the most powerful geo-processing production systems to date,” Lamont says. “Our Intel Xeon Phi powered solutions enable interactive processing and imaging from each of our geophysicist’s individual computers. A testing regime that once took weeks can now be achieved in days. Production on the cluster that once took from weeks to months, now takes days as well.
In a market where cost and time are tight, DUG continues its commitment to development, innovation and research,” Lamont concludes. “SGI and Intel’s thorough understanding of our business and the needs of our clients has created a trusted relationship based on innovation and service reliability that helps us remain competitive in a tough market.”
These shortened turn-around times allow the company to more thoroughly investigate the complex geophysical challenges brought to it by its oil and gas customers. “A field can potentially be brought online months earlier, saving millions of dollars,” notes Lamont.
Looking for more great content like this? The Print ‘n Fly Guide to SC14 in New Orleans is now available for download. We also have the Mobile Edition below to make it easier to access on your smart phone.
Table of Contents: Print ‘n Fly Guide to SC14 New Orleans
- Entering the Era of Code Modernization – Welcome Letter from Raj Hazra, Intel Vice President, Data Center Group & General Manager, Technical Computing Group
- Celebrating Year One – the Intel Parallel Computing Center Program’s First Anniversary: A Q&A with Bob Burroughs, Intel Director of Technical Computing Ecosystem Enabling
- Intel Xeon Phi Takes DownUnder GeoSolutions to New Depths
- This is one Show You Won’t Want to Miss: The Parallel Universe Computing Challenge Returns to SC14
- Meet Me at the Hub. The Intel Community Hub – new for SC14.
- SC14 Intel Booth Guide
- City Guide: Safety and Transportation Around New Orleans
- Local’s Guide to New Orleans Cuisine
- Leveraging Parallelism on Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors and Multicore Processor
- Seismic Code Modernization Yields Petascale Performance and Gordon Bell Award Nomination
As a supplement to the guide, we also offer this Sci-Fi Original story by Rich Brueckner: Angels of Silence. We hope you can enjoy it on your flight to New Orleans.