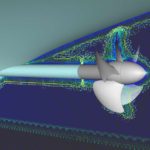
Altair has acquired Germany-based FluiDyna GmbH, a renowned developer of NVIDIA CUDA and GPU-based Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and numerical simulation technologies in whom Altair made an initial investment in 2015. FluiDyna’s simulation software products ultraFluidX and nanoFluidX have been available to Altair’s customers through the Altair Partner Alliance and also offered as standalone licenses. “We are excited about FluiDyna and especially their work with NVIDIA technology for CFD applications,” said James Scapa, Founder, Chairman, and CEO at Altair. “We believe the increased throughput and lower cost of GPU solutions is going to allow for a significant increase in simulations which can be used to further impact the design process.”
Search Results for: cfd
New Pointwise Release Adds Mesh Automation and Adaptability for CFD
Pointwise has released Version 18.1, a major update to its computational fluid dynamics (CFD) mesh generation software. With its origins in a multiyear development effort funded by the U.S. Air Force for overset grid assembly, this latest Pointwise release includes a suite of tools that provide increased automation and flexibility in mesh topology creation, mesh types and mesh quality assessment. “This release is the culmination and commercial manifestation of a two-year $1.2 million research and development effort funded by the U.S. Air Force Materiel Command, Arnold Engineering Development Complex,” said Nick Wyman, Pointwise’s director of applied research. “That effort in turn was an extension of a previous, two-year, Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) Phase II award. While focused on overset grid assembly, the capabilities added to the software are applicable to virtually any type of mesh generation.”
Unstructured-Grid CFD Algorithms at NASA on Volta GPUs
Eric Nielsen from NASA gave this talk at SC17 in Denver. “In the field of computational fluid dynamics, the Navier-Stokes equations are often solved using an unstructured-grid approach to accommodate geometric complexity. Furthermore, turbulent flows encountered in aerospace applications generally require highly anisotropic meshes, driving the need for implicit solution methodologies to efficiently solve the discrete equations. To prepare NASA Langley Research Center’s FUN3D CFD solver for the future HPC landscape, we port two representative kernels to NVIDIA Pascal and Volta GPUs and present performance comparisons with a common multi-core CPU benchmark.”
Exaflow: Collaborating on the Computational Challenges of CFD
“Fluid Dynamics (FD) simulations provide a powerful tool for the analysis of such fluid flows and are an essential element of many industrial and academic problems. The complexities and nature of fluid flows, often combined with problems set in open domains, implies that the resources needed to computationally model problems of industrial and academic relevance is virtually unbounded.”
Pointwise Adds Script Language Support for CFD Mesh Generation
Today Pointwise announced that the latest release of their CFD mesh generation software has been extended such that its Tcl-based Glyph scripting language can be called from any scripting language including Python. This new Glyph Server feature was motivated by a user’s presentation at the Pointwise User Group Meeting 2016. “The Glyph Server idea arose after talking to the customer who presented his work on ‘A Python Binding for the Pointwise Glyph Scripting Language’ at our user group meeting,” said John Chawner, Pointwise’s president. “Not only were we able to share new code with the customer to simplify his work but the conversation made us realize how to make Glyph callable from any scripting language.”
ExaFLOW Funds CFD Research for Exascale
The ExaFLOW project has announced 3.3 Million Euros of funding for a group of eight organizations to take Europe’s CFD community one step closer to performing simulations in exascale environments.
Powering Aircraft CFD with the Piz Daint Supercomputer
The Piz Daint supercomputer at the Swiss National Supercomputing Centre (CSCS) is again assisting researchers in competition for the prestigious Gordon Bell prize. “Researchers led by Peter Vincent from Imperial College London have made this year’s list of finalists for the Gordon Bell prize, with the backing of Piz Daint at the Swiss National Supercomputing Centre. The prize is awarded annually in November at SC, the world’s largest conference on supercomputing. It honors the success of scientists who are able to achieve very high efficiencies for their research codes running on the fastest supercomputer architectures currently available.”
Pegasus 5 CFD Program Wins NASA’s Software of the Year
Over at NASA, Michelle Moyers writes that the 2016 NASA Software of the Year Award has gone to Pegasus 5, a revolutionary CFD tool. “Developed in-house by a team led by aerospace engineer Stuart Rogers from NASA Ames, Pegasus 5 has been used for aerodynamic modeling and simulation by nearly every NASA program over the past 15 years, including the space shuttle, the next-generation Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System, and commercial crew programs.”
CFMS Joins Hyperflux++ Project to Advance CFD
Today the Centre for Modeling & Simulation (CFMS) in the UK announced it will be taking part in a follow-on to the Hyperflux project. “Hyperflux ++ builds on the successful Innovate UK project ‘Hyperflux’ – developing next generation CFD technology for the civil, automotive, renewable and aerospace sectors.”
New CFD and Geometry Interfaces in Pointwise Meshing Software
Today Pointwise announced the latest release of its meshing software featuring updated native interfaces to computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and geometry codes. Pointwise Version 17.3 R5 also includes geometry import and export to the native file format of Pointwise’s geometry kernel and a variety of bug fixes.