Intel and the National Science Foundation (NSF), joint funders of the Machine Learning for Wireless Networking Systems (MLWiNS) program, today announced recipients of awards for research projects into ultra-dense wireless systems that deliver the throughput, latency and reliability requirements of future applications – including distributed machine learning computations over wireless edge networks. Here are the […]
New Memristors at MIT: Networks of Artificial Brain Synapses for Neuromorphic Devices
A possible glimpse at a future form of high performance edge computing – networks of artificial brain synapses – developed by engineers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology is showing promise as a new memristor design for neuromorphic devices, which mimic the neural architecture in the human brain. Published today in Nature Nanotechnology, results of […]
Purdue’s ‘Anvil’ to Be Driven by Dell, AMD ‘Milan’ CPUs, Nvidia A100 Tensor Core GPUs
Another in a series of National Science Foundation supercomputing awards has been announced, this one a $10 million funding for a system to be housed at Purdue University to support HPC and AI workloads and scheduled to enter production next year. The system, dubbed Anvil, will be built in partnership with Dell and AMD and […]
NSF awards compute time on Frontera Supercomputer for 49 projects
The most powerful supercomputer in the world for academic research has established its mission for the coming year. “The NSF has approved allocations of supercomputing time on Frontera to 49 science projects for 2020-2021. Time on the TACC supercomputer is awarded based on a project’s need for very large scale computing to make science and engineering discoveries, and the ability to efficiently use a supercomputer on the scale of Frontera.”
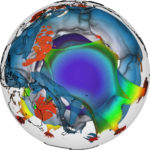
Simulating the Earth’s mysterious mantle
Scientists are taking advantage of an $2.5 million NSF grant to develop a new framework for integrated geodynamic models that simulate the Earth’s molten core. “Most physical phenomena can be described by partial differential equations that explain energy balances or loss,” said Heister, an associate professor of mathematical sciences who will receive $393,000 of the overall funding. “My geoscience colleagues will develop the equations to describe the phenomena and I’ll write the algorithms that solve their equations quickly and accurately.”
The Role of Cyberinfrastructure in Science: Challenges and Opportunities
Ewa Deelman from the University of Southern California gave this Invited Talk at SC19. “This presentation examines selected modern scientific discoveries, such as the detection of gravitational waves from the CI perspective. It aims to answer the following key questions: first, what were the key CI solutions that enabled a particular scientific result? and second, what were the challenges that needed to be overcome?”
SDSC Conducts 50,000+ GPU Cloudburst Experiment with Wisconsin IceCube Particle Astrophysics Center
In all, some 51,500 GPU processors were used during the approximately two-hour experiment conducted on November 16 and funded under a National Science Foundation EAGER grant. The experiment used simulations from the IceCube Neutrino Observatory, an array of some 5,160 optical sensors deep within a cubic kilometer of ice at the South Pole. In 2017, researchers at the NSF-funded observatory found the first evidence of a source of high-energy cosmic neutrinos – subatomic particles that can emerge from their sources and pass through the universe unscathed, traveling for billions of light years to Earth from some of the most extreme environments in the universe.
NSF Invests in Multi-Messenger Astrophysics
“The promise of multi-messenger astrophysics, however, can be realized only if sufficient cyberinfrastructure is available to rapidly handle, combine and analyze the very large-scale distributed data from all types of astronomical measurements. The conceptualization phase of SCIMMA will balance rapid prototyping, novel algorithm development and software sustainability to accelerate scientific discovery over the next decade and more.”
HPC Framework Blocks to Ease Programming of Exascale Supercomputers
Researchers are beginning a three-year cross-institute project that aims to lower the barrier to entry for software engineers developing new high-performance applications on large scale parallel systems. “The team of researchers plan to combine user insights, new compiler optimizations, and advanced runtime support to create the PAbB framework which will ultimately create building blocks of parallel code for heterogeneous environments to use across a number of applications from computational science and data science.”
NSF Grant to help develop cyberinfrastructure across Midwest
The National Science Foundation has awarded a $1.4 million grant to a team of experts led by Timothy Middelkoop, assistant teaching professor of industrial and manufacturing systems engineering in the University of Missouri’s College of Engineering. The researchers said the grant will fill an emerging need by providing training and resources in high-performance computer systems. “There is a critical need for building cyberinfrastructure across the nation, including the Midwest region,” said Middelkoop, who also serves as the director of Research Computing Support Services in the Division of Information Technology at MU. “It is our job as cyberinfrastructure professionals to facilitate research and work with researchers as a team to identify the best practices.”